
Credit Scores Explained
Your credit score is one of the most important factors that determine your ability to access credit and loans. IndigoCard aims to help users understand credit scores better and also provide tips to improve them.
What is a Credit Score?
A credit score is a three-digit number ranging between 300-850 that represents a snapshot of your creditworthiness. It is based on your credit history and activity.
Credit scores are generated by credit bureaus like Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax. Lenders use these scores to evaluate how likely you are to repay debts.
Definition of credit scores
In simple terms, a credit score is a numerical expression of your creditworthiness. It indicates your ability to manage debts and make timely repayments.
A higher score signifies lower credit risk while a lower score translates to higher risk for lenders. Credit scores enable lenders to quickly make lending decisions based on your reliability as a borrower.
Importance of credit scores
Maintaining a good credit score is important for several reasons:
- Affects the ability to access loans and credit cards
- Determines eligibility for mortgages
- Influences interest rates on credit
- Indicates reliability to lenders
- Even rental and job applications may require credit checks
Factors that determine credit score
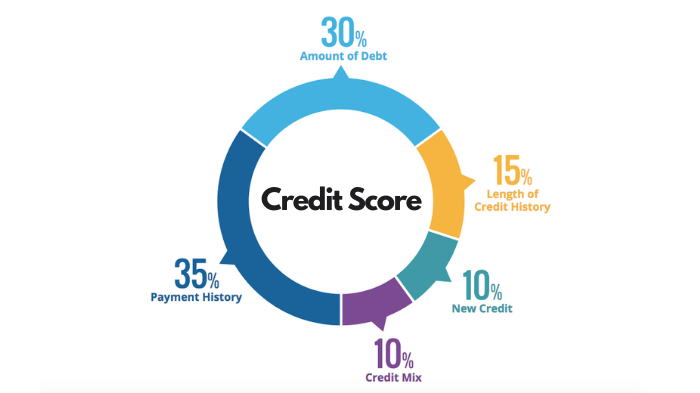
The main factors that impact your credit score are:
- Payment history – track record of on-time repayments
- Total owed – amounts owed across types of credit
- Credit history length – how long you have maintained accounts
- New credit – number of new accounts opened
- Credit mix – a variety of credit accounts like mortgages, auto loans, cards etc.
Checking Your Credit Score
It is advisable to check your credit score frequently to monitor where you stand. Here’s what you need to know:
Why check your credit score regularly
- Detect any errors or fraudulent activities.
- Review the health of your credit.
- Assess if you need to take action to improve it.
- Keep tabs on factors negatively impacting your score.
Where to get your credit score report
You can obtain credit reports from agencies like Experian, TransUnion and Equifax. Many credit card companies also offer free access to your credit score.
Understanding your credit score report
The credit report provides your score and details on the five factors impacting it – payment history, credit utilization, history length, new credit and credit mix.
Review the factors where you may be losing points, like missed payments or high balances. This will give you areas to focus on for improvement.
Improving Your Credit Score
Here are some tips to improve your credit score:
Tips for boosting your credit score
- Make payments on time each month
- Lower credit utilization ratio
- Pay down balances rather than moving debt around
- Don’t close unused credit accounts
- Review reports and dispute errors
- Limit new credit applications
Strategies for credit score improvement
- Set up automatic payments
- Keep balances low on cards
- Pay more than minimum
- Maintain a long history with the same accounts
- Mix types of credit accounts
Timeframe for increasing credit score
Scores respond relatively fast to credit repair efforts. You can see improvements in as little as a month. However, it takes 6 months to a year to achieve significant score increases.

Credit Score Ranges
Credit scores fall under different ranges, which are viewed as:
Different score ranges
- 800-850 = Excellent
- 740-799 = Very Good
- 670-739 = Good
- 580-669 = Fair
- 300-579 = Poor
Good and bad credit scores
Scores above 700 are generally viewed as good while those below 600 are considered bad by most lenders. The higher your score, the better your creditworthiness.
Impact of credit score range on interest rates
Higher scores qualify you for lower interest rates on loans and credit cards. People with lower scores pay higher rates or are denied credit.
Factors Affecting Your Credit Score
Here are the key factors that impact your credit score and how they are evaluated:
Payment history
- Most important factor
- Assesses records of on-time payments
- Missed and late payments lower scores
Credit utilization
- Measures the ratio of balances to credit limits on cards and loans
- High utilization lowers scores
- The ideal ratio is below 30%
Credit history length
- Check the age of your credit accounts
- Long credit history with the same accounts boosts score
New credit applications
- Opening many new accounts in a short span reduces the score
- But a mix of new credit also helps over time
Credit mix
- Variety of credit accounts – mortgage, cards, car loans, etc improve scores
- Managing different types responsibly increases creditworthiness

How IndigoCard Can Help
IndigoCard aims to help you monitor and improve your credit score by:
- Viewing your score and trends right on the app dashboard
- Getting personalized tips to boost your score
- Letting you see the impact your spending has on your score
- Sending timely alerts on factors influencing your credit score
- Helping improve your credit mix with the responsible use of IndigoCard
With IndigoCard, you have a trusted partner to keep your credit healthy and achieve your financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A credit score is calculated based on the information in your credit reports from the three major credit bureaus. Scores factor in payment history, credit utilization, history length, new credit, and credit mix. Complex algorithms are used to give each factor a specific weight to calculate the score.
No, checking your credit score does not lower it. Soft inquiries you make to view your scores from credit bureaus do not impact the score. Only hard inquiries made when applying for new credit are considered.
Yes, your history of utility payments like electricity, gas, phone bills, etc. can influence your credit score. Timely payments reflect positively while missed payments can lower your score.
No, debit cards do not help build credit history as the payments are deducted directly from your bank account. Only credit cards that you repay over time are reported to the bureaus and affect scores.
Even after you close the credit card or loan accounts, they continue to be reported on your credit report and impact scores for about 10 years from the date of closing.
Yes, credit scores can fluctuate slightly monthly based on your credit activities and any changes reported to the credit bureaus. Major fluctuations are generally not common if your habits remain consistent.
Yes, your age does influence your credit score to some extent, since it is harder to establish a long credit history and mix of accounts when you are younger. Scores tend to improve with age.
No, your income is not a factor in calculating your credit score. However, lenders may consider income details separately when making lending decisions in addition to your score.
Yes, since the three major credit bureaus may have some differences in the data they collect and report about you, you may have slightly different credit scores with each bureau.
Most negative information stays on your credit report for about 7 years from the date of the incident. Bankruptcy records stay for 10 years. So they continue to impact your scores during this time.